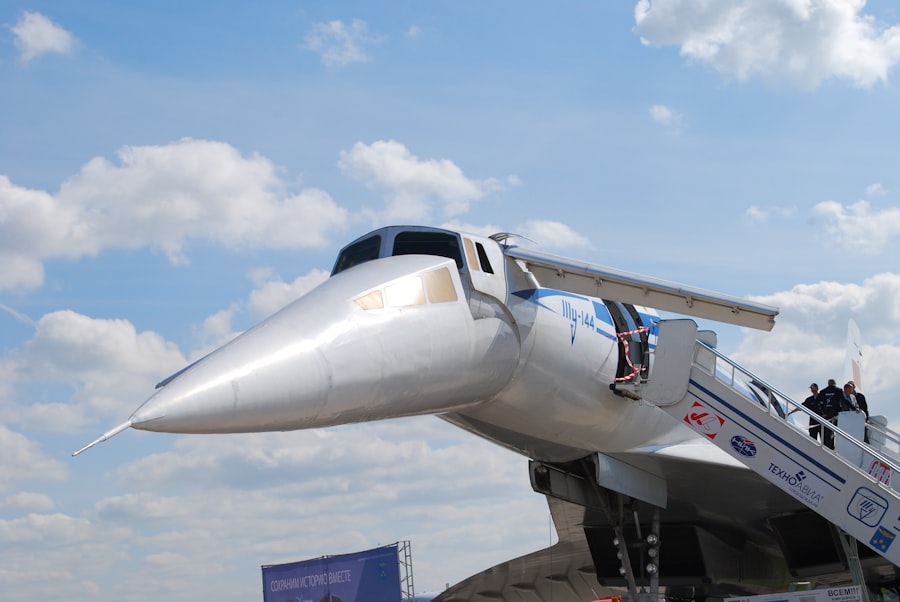
The Concorde, a marvel of engineering and design, was born out of a collaborative effort between British and French aerospace industries. The project began in the early 1960s, driven by a desire to push the boundaries of commercial aviation. The British Aircraft Corporation (BAC) and Aérospatiale, the French state-owned aerospace manufacturer, joined forces to create an aircraft that could travel faster than the speed of sound.
This ambitious endeavor was not merely about speed; it was about redefining the very nature of air travel. The Concorde’s design was characterized by its sleek, delta-wing shape, which allowed it to slice through the air with minimal drag, a crucial factor for achieving supersonic speeds. The development of the Concorde was fraught with challenges, including technical hurdles and political considerations.
The aircraft’s first flight took place on March 2, 1969, in Toulouse, France, marking a significant milestone in aviation history. The prototype’s successful takeoff was a testament to the ingenuity and determination of the engineers and designers who had poured their expertise into the project. However, the journey to commercial service was not straightforward.
The Concorde faced skepticism from various quarters, including concerns about noise pollution and environmental impact. Despite these challenges, the aircraft was eventually certified for commercial operations in 1976, heralding a new era in air travel.
The Concorde was not alone in its quest for supersonic travel; it faced competition from several other aircraft projects during its development. Notably, the Soviet Union’s Tupolev Tu-144 was developed concurrently and made its first flight just months before the Concorde. While both aircraft shared the ambition of breaking the sound barrier, they differed significantly in design philosophy and operational capabilities.
The Tu-144 was larger and had a higher passenger capacity, but it suffered from reliability issues and a troubled operational history that ultimately led to its retirement after only a few years of service. In contrast, the Concorde became synonymous with luxury and exclusivity. It was designed to carry a maximum of 100 passengers, offering an experience that was as much about comfort as it was about speed.
The aircraft’s cruising speed of Mach 2 allowed it to reduce transatlantic flight times significantly—New York to London could be completed in under three hours. This capability positioned the Concorde as a premium option for business travelers and affluent individuals seeking to maximize their time. While other aircraft like the Boeing 747 revolutionized air travel by making it accessible to the masses, the Concorde catered to a niche market that valued speed and luxury above all else.
Key Takeaways
- The Concorde was a game-changing aircraft that revolutionized supersonic travel.
- The Concorde offered a luxurious and comfortable experience at twice the speed of sound.
- The Concorde had a significant impact on global travel and business, setting new standards for efficiency and prestige.
- The tragic end of the Concorde marked the conclusion of an era in aviation history.
- The Concorde’s legacy continues to influence modern aviation and inspire future developments in supersonic travel.
The Concorde Experience: Luxury and Comfort at Mach 2
Flying on the Concorde was an experience unlike any other in commercial aviation. From the moment passengers stepped aboard, they were enveloped in an atmosphere of elegance and sophistication. The cabin featured plush seating arranged in a two-by-two configuration, allowing for greater privacy and comfort compared to the more crowded layouts of conventional airliners.
The interior design incorporated high-quality materials, including leather upholstery and fine wood finishes, creating an ambiance that reflected the exclusivity of the service. In addition to its luxurious surroundings, the Concorde offered an array of amenities that catered to its discerning clientele. Passengers were treated to gourmet meals prepared by renowned chefs, accompanied by an extensive selection of fine wines and champagnes.
The service was impeccable, with highly trained flight attendants dedicated to ensuring that every need was met during the flight. Moreover, the unique experience of flying at supersonic speeds added an exhilarating dimension to air travel; passengers could witness breathtaking views from their windows as they soared above the clouds at altitudes exceeding 60,000 feet.
Concorde’s Impact on Global Travel and Business

The introduction of the Concorde had a profound impact on global travel and business dynamics. By significantly reducing flight times between major cities, it transformed how executives and business leaders approached international travel. The ability to cross the Atlantic in under three hours meant that meetings could be scheduled with greater flexibility, allowing for same-day round trips between New York and London or Paris.
This efficiency not only benefited individual travelers but also had broader implications for international business operations. Moreover, the Concorde became a symbol of prestige and innovation in aviation. Its presence on the tarmac at airports around the world signified a new era of travel that combined speed with luxury.
Airlines that operated the Concorde—primarily British Airways and Air France—leveraged this image to attract high-profile clients and enhance their brand reputation. The aircraft’s allure extended beyond its operational capabilities; it became a cultural icon featured in films, documentaries, and advertisements, further embedding itself into the public consciousness as a representation of modernity and technological advancement.
The Tragic End: The Concorde’s Final Flight
| Event | Details |
|---|---|
| Date | July 25, 2000 |
| Location | Paris, France |
| Aircraft | Air France Flight 4590 |
| Cause | Engine failure and subsequent fire |
| Fatalities | All 109 passengers and crew on board, plus 4 on the ground |
| Consequences | Immediate grounding of the Concorde fleet and eventual retirement of the aircraft |
Despite its groundbreaking achievements, the Concorde’s legacy was marred by tragedy. On July 25, 2000, Air France Flight 4590 crashed shortly after takeoff from Charles de Gaulle Airport in Paris, resulting in the loss of all 109 people on board and four individuals on the ground. The accident was attributed to a series of unfortunate events that began when a piece of metal debris from a preceding aircraft punctured one of the Concorde’s tires during takeoff.
This led to a catastrophic failure that ultimately caused the aircraft to crash into a hotel in Gonesse. The aftermath of this disaster had far-reaching consequences for the Concorde program. Following the crash, both British Airways and Air France suspended their Concorde operations while investigations were conducted.
Although safety modifications were implemented, including changes to tire design and improved maintenance protocols, public confidence in supersonic travel had been severely shaken. The combination of rising operational costs, declining passenger numbers post-9/11, and heightened safety concerns ultimately led to the retirement of the Concorde in 2003.
The Legacy of the Concorde: Influence on Modern Aviation
The legacy of the Concorde extends far beyond its operational lifespan; it has left an indelible mark on modern aviation that continues to influence aircraft design and development today. Its pioneering work in supersonic flight has inspired subsequent generations of engineers and designers who seek to push the boundaries of what is possible in air travel. The technological advancements achieved during the Concorde’s development—such as advancements in aerodynamics, materials science, and engine technology—have been integrated into contemporary aircraft designs.
Moreover, the Concorde’s emphasis on passenger experience has set a benchmark for luxury air travel that persists today. Airlines continue to draw inspiration from its model of providing exceptional service and comfort for premium passengers. While commercial aviation has evolved significantly since the days of the Concorde, its influence can be seen in modern business class offerings that prioritize space, privacy, and high-quality dining experiences.
The Future of Supersonic Travel: Lessons from the Concorde

As interest in supersonic travel resurges with advancements in technology and growing demand for faster air travel options, lessons learned from the Concorde’s history are invaluable. Current projects like Boom Supersonic’s Overture aim to create a new generation of supersonic aircraft that address some of the challenges faced by their predecessor. These modern designs focus on reducing noise pollution through innovative engine technology and aerodynamic improvements while also considering environmental sustainability—a critical factor that was often overlooked during the Concorde’s era.
Additionally, there is a renewed emphasis on safety protocols and regulatory compliance as new supersonic aircraft are developed. The tragic accident involving Air France Flight 4590 serves as a stark reminder of the importance of rigorous safety standards in aviation. As companies explore ways to reintroduce supersonic travel into commercial aviation, they must prioritize not only speed but also safety and environmental responsibility to gain public trust.
Remembering the Concorde: Celebrating its Innovation and Achievement
The Concorde remains an enduring symbol of human ingenuity and ambition in aviation history. Its ability to traverse vast distances at unprecedented speeds captured the imagination of travelers around the world and set new standards for what could be achieved in commercial flight. As we reflect on its legacy, it is essential to celebrate not only its technological achievements but also its cultural significance as an icon of luxury travel.
Museums around the world have preserved Concordes as artifacts of this remarkable era in aviation history, allowing future generations to appreciate its design and engineering marvels firsthand. Events commemorating its flights continue to draw enthusiasts who share stories about their experiences aboard this extraordinary aircraft. In doing so, we honor not just an aircraft but an era defined by innovation, aspiration, and a relentless pursuit of excellence in air travel.